Hypertriglyceridemia remains a major challenge in cardiovascular care, linked with increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and pancreatitis. While lifestyle modifications and current lipid-lowering therapies can help, many patients still require additional treatment options. The Essence-TIMI 73b trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine (August 2025), brings promising results for olezarsen, a novel triglyceride-lowering therapy.
Study Overview
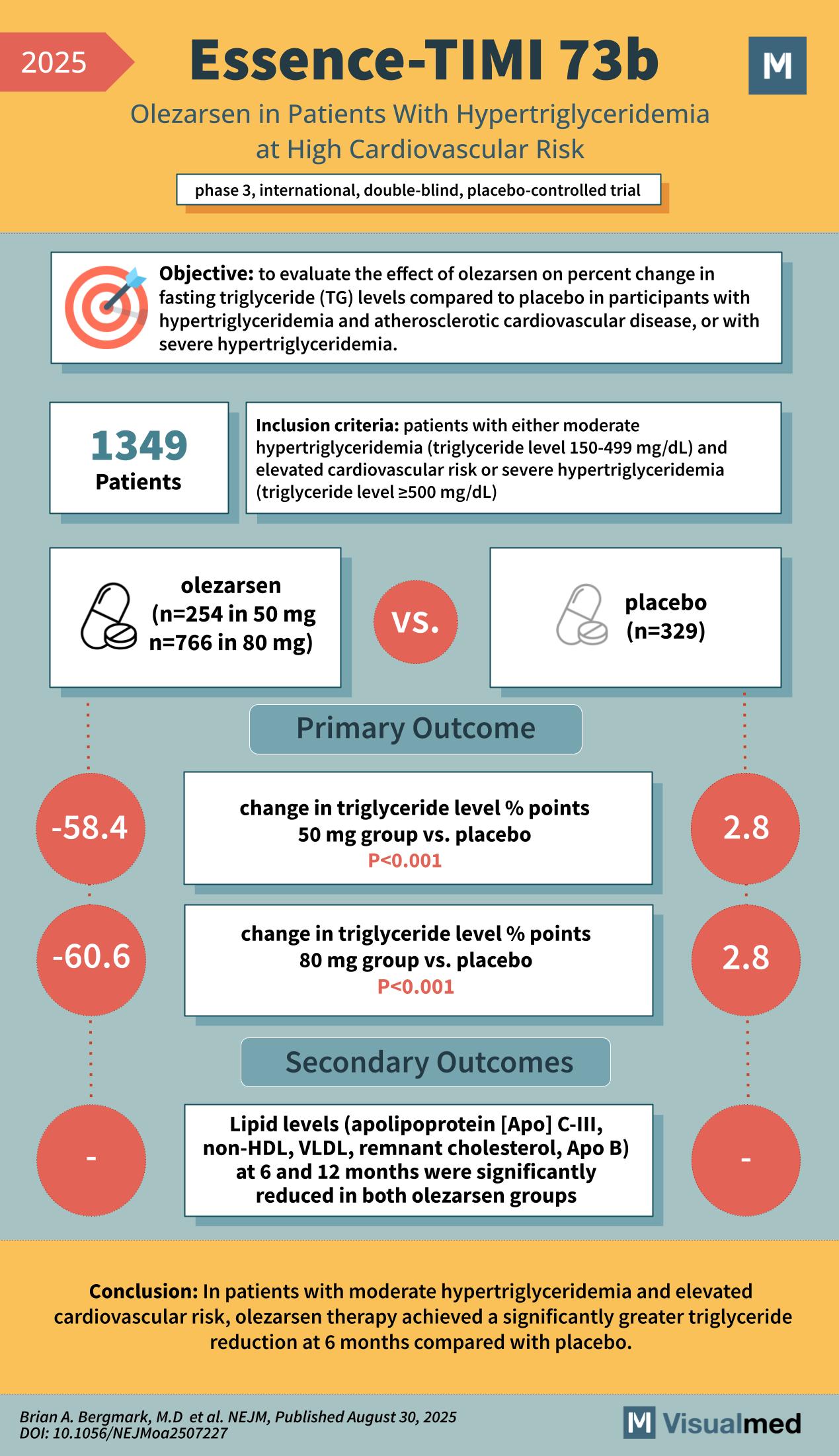
- Design: Phase 3, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- Patients: 1,349 individuals with either:
- Moderate hypertriglyceridemia (TG 150–499 mg/dL) plus elevated cardiovascular risk, or
- Severe hypertriglyceridemia (TG ≥500 mg/dL)
- Groups:
- Olezarsen 50 mg (n=254)
- Olezarsen 80 mg (n=766)
- Placebo (n=329)
Objective: To evaluate the effect of olezarsen on percent change in fasting triglyceride levels compared with placebo.
Key Results
Primary Outcome: Triglyceride Reduction at 6 Months
- Olezarsen 50 mg: –58.4% vs. placebo (+2.8%), P<0.001
- Olezarsen 80 mg: –60.6% vs. placebo (+2.8%), P<0.001
Both doses achieved striking reductions in triglyceride levels compared to placebo.
Secondary Outcomes: Lipid Markers
Significant reductions at 6 and 12 months in:
- Apolipoprotein C-III (Apo C-III)
- Non-HDL cholesterol
- VLDL cholesterol
- Remnant cholesterol
- Apolipoprotein B (Apo B)
These findings support olezarsen’s broader impact on atherogenic lipoproteins.
Clinical Implications
In patients with moderate hypertriglyceridemia and elevated cardiovascular risk, olezarsen achieved robust and clinically meaningful triglyceride lowering. This positions it as a potentially important therapy for patients not adequately managed by current treatments.
Future studies will be critical to determine whether these lipid changes translate into reductions in cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular death.
Conclusion
The Essence-TIMI 73b trial demonstrates that olezarsen therapy provides substantial reductions in triglyceride and atherogenic lipid levels compared with placebo. For clinicians managing high-risk patients with persistent hypertriglyceridemia, these results highlight an emerging therapeutic option that could reshape lipid management strategies.
📖 Reference:
Bergmark BA, et al. Essence-TIMI 73b: Olezarsen in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia at High Cardiovascular Risk. NEJM. Published August 30, 2025. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2507227