The RESCUE-ASDH Trial: Craniotomy vs. Decompressive Craniectomy
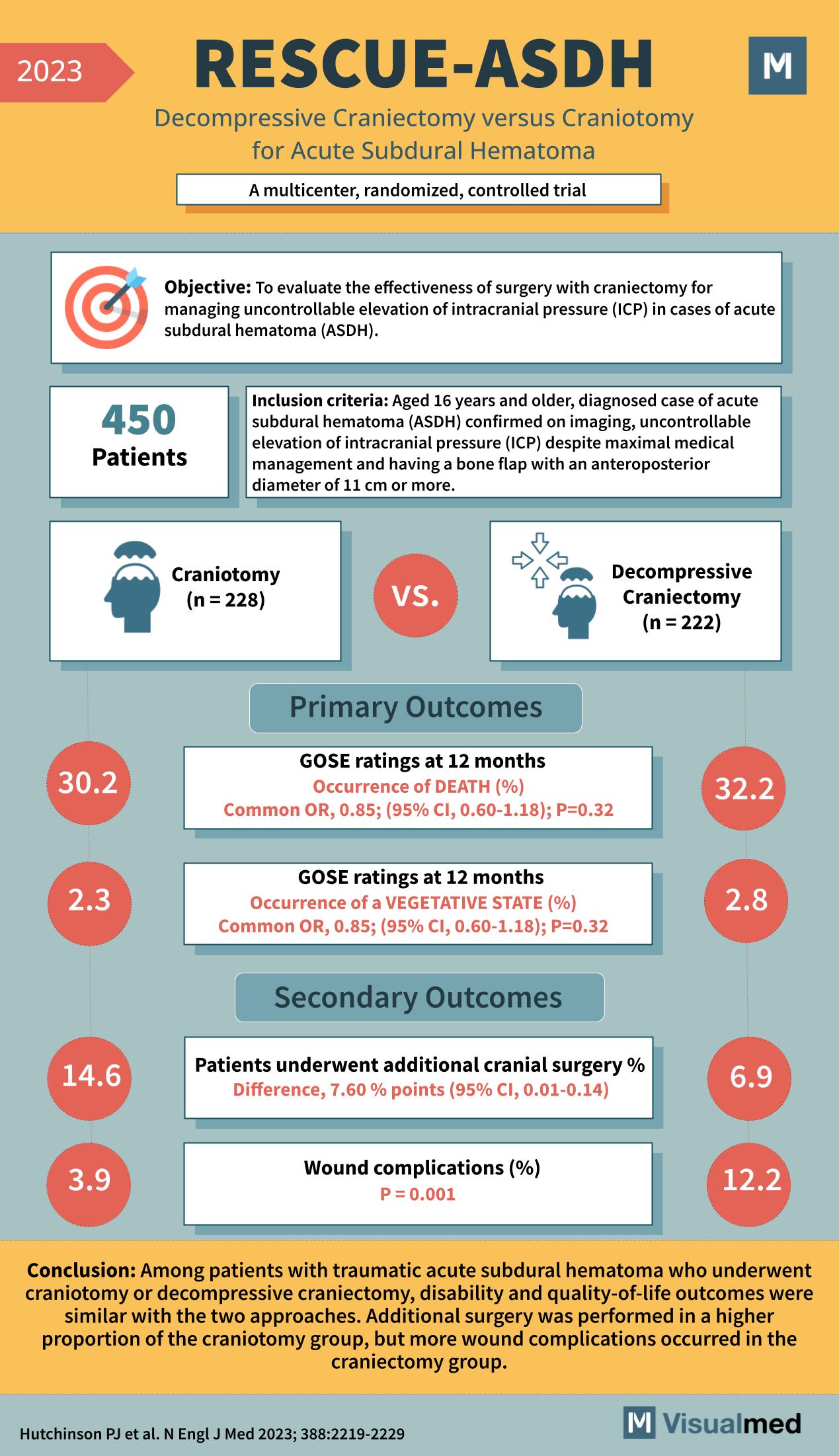
The RESCUE-ASDH Trial, conducted in 2023, was a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial that played a crucial role in understanding the management of acute subdural hematoma (ASDH), a severe brain injury.
Objective of the RESCUE-ASDH Trial
The trial aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of craniotomy versus decompressive craniectomy in managing uncontrollable intracranial pressure in patients with ASDH.
Enrollment and Criteria
The study included 450 patients aged 16 years and older diagnosed with ASDH, exhibiting elevated intracranial pressure despite maximal medical management, and requiring a bone flap of 11 cm or more.
Interventions
Participants were randomly assigned to undergo either craniotomy (228 patients) or decompressive craniectomy (222 patients).
Results of the RESCUE-ASDH Trial
Primary Outcomes
- The Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended (GOSE) ratings at 12 months post-surgery showed no significant difference in the occurrence of death between the craniotomy group (30.2%) and the decompressive craniectomy group (32.2%).
- The occurrence of a vegetative state was also similar between the two groups, with 2.3% in the craniotomy group and 2.8% in the craniectomy group.
Secondary Outcomes
- Additional cranial surgery was required more often in the craniotomy group (14.6%) than in the craniectomy group (6.9%).
- The craniectomy group had a higher rate of wound complications (12.2%) compared to the craniotomy group (3.9%).
Conclusion and Implications
The RESCUE-ASDH Trial concluded that disability and quality-of-life outcomes were similar for patients with ASDH whether they underwent craniotomy or decompressive craniectomy. However, additional surgery was more common in the craniotomy group, while wound complications were more prevalent in the craniectomy group. This trial informs surgical decision-making, balancing the risks and benefits of two different surgical approaches for ASDH.