VESALIUS-CV Trial (2025)
Evolocumab in Patients without a Previous Myocardial Infarction or Stroke
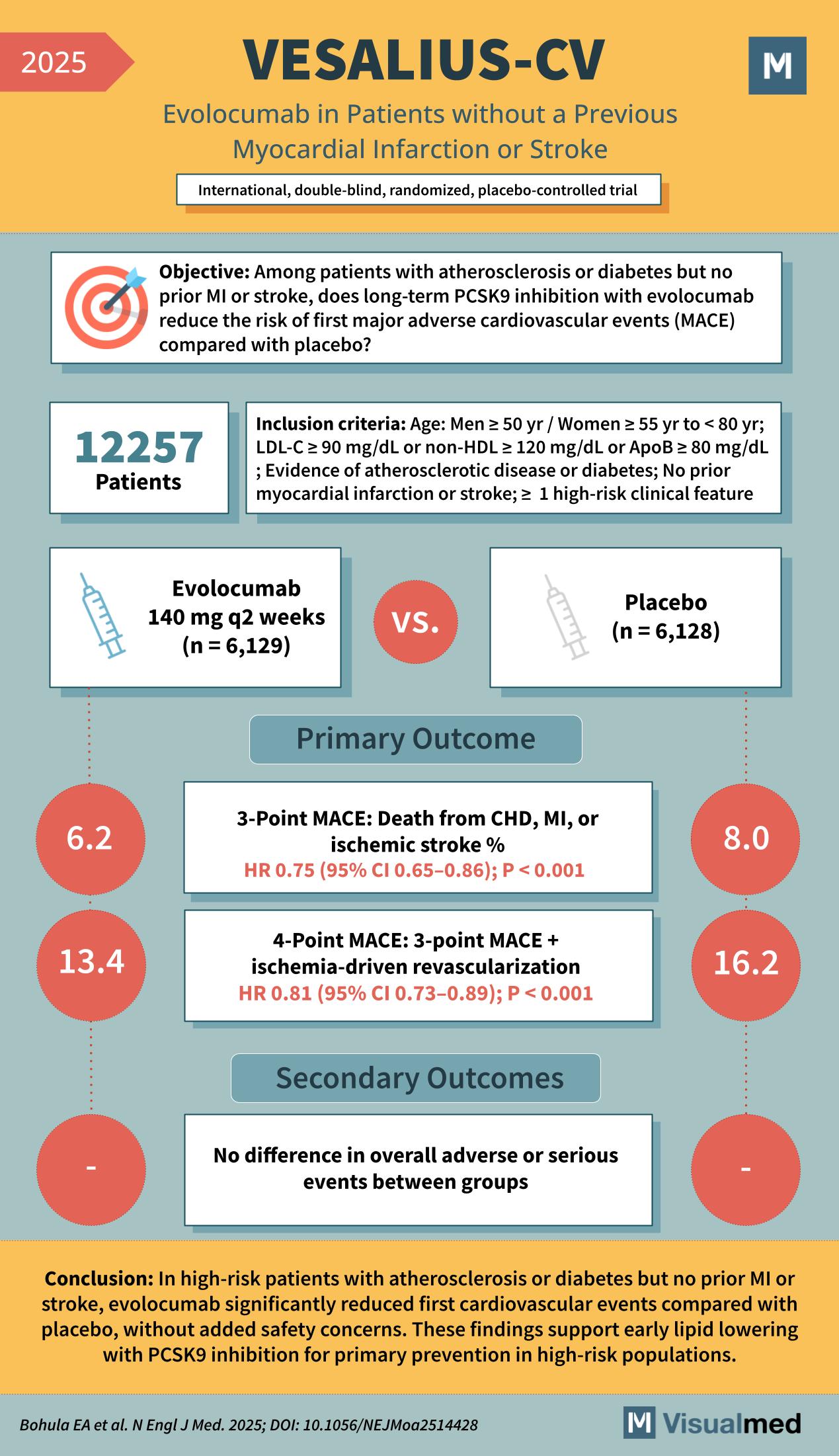
International, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Objective:
Among patients with atherosclerosis or diabetes but no prior MI or stroke, does long-term PCSK9 inhibition with evolocumab reduce the risk of first major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) compared with placebo?
Inclusion Criteria:
- Age: Men ≥ 50 yr / Women ≥ 55 yr to < 80 yr
- LDL-C ≥ 90 mg/dL or non-HDL ≥ 120 mg/dL or ApoB ≥ 80 mg/dL
- Evidence of atherosclerotic disease (coronary, cerebrovascular, or peripheral) or diabetes
- No prior myocardial infarction or stroke
- At least 1 high-risk clinical feature
Population:
12,257 patients (median age 66 yr; 43% women)
- Evolocumab 140 mg q2 weeks (n = 6,129)
vs. - Placebo (n = 6,128)
Median follow-up: 4.6 years
Primary Outcomes:
3-Point MACE: Death from CHD, MI, or ischemic stroke
- Evolocumab 6.2% vs Placebo 8.0%
- HR 0.75 (95% CI 0.65–0.86); P < 0.001
4-Point MACE: 3-point MACE + ischemia-driven revascularization
- Evolocumab 13.4% vs Placebo 16.2%
- HR 0.81 (95% CI 0.73–0.89); P < 0.001
Safety:
- No difference in overall adverse or serious events between groups
Conclusion:
In high-risk patients with atherosclerosis or diabetes but no prior MI or stroke, evolocumab significantly reduced first cardiovascular events compared with placebo, without added safety concerns. These findings support early lipid lowering with PCSK9 inhibition for primary prevention in high-risk populations.
Citation:
Bohula EA et al. N Engl J Med. 2025; DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2514428