The ACORN Trial: Cefepime vs. Piperacillin-Tazobactam’s Impact on Renal Outcomes
In 2023, the ACORN Trial set out to investigate the renal and neurological outcomes of hospitalized adults with acute infections treated with two common antibiotics, providing valuable insights for healthcare providers.
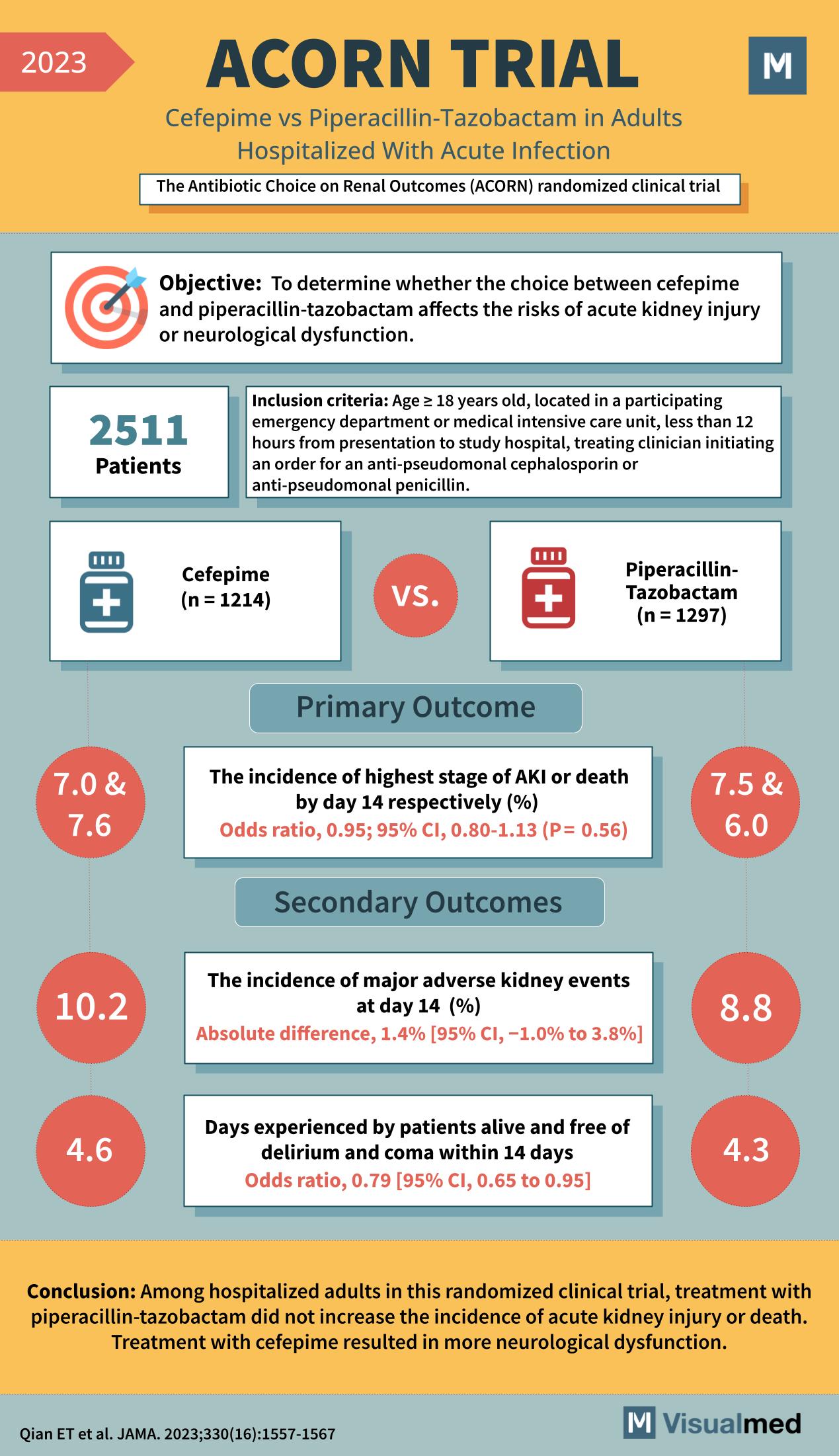
Objective of the ACORN Trial
This randomized clinical trial aimed to determine if the choice between cefepime and piperacillin-tazobactam affects the risks of acute kidney injury (AKI) or neurological dysfunction in hospitalized adults.
Study Design and Patient Selection
With 2511 participants, the trial included adults from emergency departments or medical intensive care units, all within 12 hours of presentation and ordered for anti-pseudomonal cephalosporin or penicillin treatment.
Comparative Analysis
Patients were divided into two treatment groups: 1214 received cefepime and 1297 were treated with piperacillin-tazobactam.
Outcomes of the ACORN Trial
Primary Outcome
- The incidence of the highest stage of AKI or death by day 14 was similar between the cefepime group (7.0%) and the piperacillin-tazobactam group (7.5%), with an odds ratio of 0.95.
Secondary Outcomes
- Major adverse kidney events at day 14 had a slight absolute difference, being higher in the cefepime group (10.2%) compared to the piperacillin-tazobactam group (8.8%).
- Days alive and free from delirium and coma within 14 days were more favorable in the cefepime group, with an odds ratio of 0.79.
Conclusions and Clinical Implications
The ACORN Trial concluded that treatment with piperacillin-tazobactam did not increase the incidence of AKI or death. However, cefepime treatment resulted in a higher incidence of neurological dysfunction. This trial provides evidence to guide antibiotic choice, balancing the risks of kidney and neurological adverse effects in patients with acute infections.