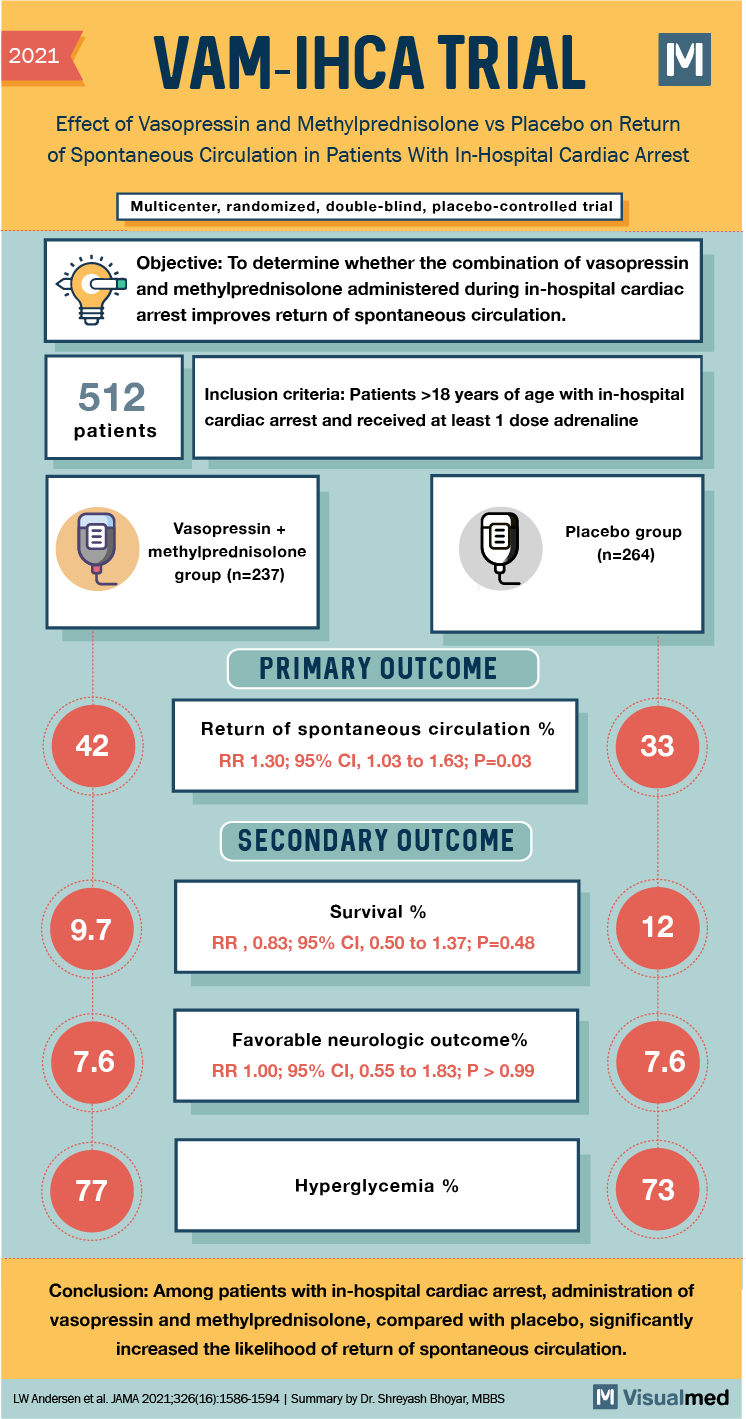
2021 VAM-IHCA TRIAL M Effect of Vasopressin and Methylprednisolone vs Placebo on Return of Spontaneous Circulation in Patients with In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Objective: To determine whether the combination of vasopressin and methylprednisolone administered during in-hospital cardiac arrest improves return of spontaneous circulation. 512 patients Inclusion criteria: Patients >18 years of age with in-hospital cardiac arrest and received at least 1 dose adrenaline Vasopressin + methylprednisolone group (n=237) Placebo group (n=264) PRIMARY OUTCOME 42 Return of spontaneous circulation % RR 1.30; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.63; P=0.03 SECONDARY OUTCOME 9.7 Survival % RR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.50 to 1.37; P=0.48 7.6 Favorable neurologic outcome% RR 1.00; 95% CI, 0.55 to 1.83; P >0.99 7.6 Hyperglycemia % Conclusion: Among patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest, administration of vasopressin and methylprednisolone, compared with placebo, significantly increased the likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation. LW Andersen et al. JAMA 2021;326(16):1586-1594